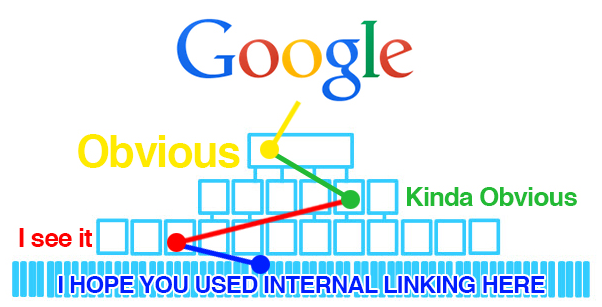
Internal linking is an essential part of SEO. Internal linking can have a huge impact on both your users, and search engines. By reviewing the concepts in this quick start guide you can get an idea of where to focus your attention. Below is an illustration of how Google moves through obvious home page and category content with it’s crawler, but has difficulty defining relationships between pages lower in the hierarchy.
Internal Linking Strategies
Internal Linking, External Linking and Inbound Links
Internal linking – when one page points to another in a domain. It allows users to navigate and discover content on your site and can occur in the navigation, the body content or the footer.
External linking – when you link to an external source.
Inbound links – links that are pointed to any of the pages in your domain from other websites across the internet.
Information Architecture(IA) vs. Internal Linking:
- It is important to recognize that your sites architecture and it’s internal linking strategies are not the same thing. IA does take up a lot of your links and needs to be managed but it doesn’t really involve the same level of depth when it comes to how you will link in your article content.
- http://moz.com/blog/site-architecture-for-seo
Types of internal links
- Anchor text
- Anchor text is the copy that is wrapped between the <a></a> tags, it is a keyword signal that helps attribute how the link is relevant to the user.
- Linked image
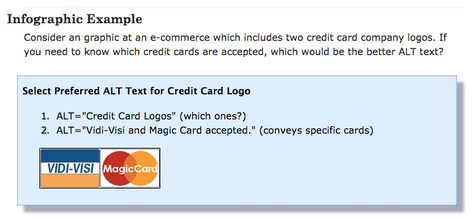
- Linked images obviously do not have text that is readable for Google, to tell the user and Google what you want – you will add an alt tag to the image. When using alt tags it is important to write as if you were describing the image to a blind person. Alt tags are an accessibility element after all.
- http://accessibility.psu.edu/images
Crawler Limitations – Below is a list of some of the limitations that crawlers have. Knowing what crawlers can and cannot view will help you avoid wasted effort.
- No Form Submits – Data collection forms sometimes have an element that submits a form then redirects a user to another page – crawlers will not submit therefore cannot use this as a vehicle.
- No search results pages – Crawlers will not use search functionality – so if the only way to find a page is by using the search you may have some difficulty!
- No JavaScript links/Flash/Java – Crawlers see plain HTML only!
- Robots.text blocks – if a webmaster blocks crawlers on a page using robots.text
- 100 link limit – There are a few reasons for the 100 link limit
- User experience – users hate ugly pages with too many links!
- Division of link juice – The SEO value spread across the site is diminished in large link volumes
- Links in Iframes – Nofollowing iframes is tricky, one of the popular methods currently is posted here:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/12611091/can-i-add-rel-nofollow-to-iframe-tag/20140084#20140084
- Benefits of Internal Linking
- Aid Navigations
- Distribute page authority
- Contribute to the content on the page
Internal Linking Tactics
- Content, content, content – you need to have something to link to that is meaningful to the user and substantial enough to be considered valuable by the crawler.
- Thematic linking – internal links are best when they are embedded in the content. This means that the linker needs to be related to the linkee.
- Use nofollow on links that lead to pages that are already crawled frequently (E.G.) Homepage and Contact us
- Do not use NoFollow to artificially sculpt the website linking – it is a waste.
- If you have found content that will be relevant to the user on an external site that has high page authority then do not be afraid to link externally to it.
- Limit the amount of internal links in each page – It needs to look natural and besides; most crawlers have a budget of pages to spider.
- Align internal linking with the redirect strategy. canonicalization.\
- Account for the 100 link limit
- Do not use large footer links unless they are useful to the user.
- Don’t overload the head navigation
- Canonicalization – Set the preferred URL for duplicate content
Conclusion
It isn’t that hard, create content – then amplify its value by tying it all together. The technical aspects are definitely something to worry about. But so long as you stick to the core principles of developing content and cross-promoting it
Want to receive more articles?
Sign-up for our weekly newsletter to receive info that will help your business grow